The ever-increasing capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have brought forth a new type of AI applications, making it possible to tackle problems in a human-like manner – often while using little to no training data (there's no getting around understanding the domain though 😉). While keeping up with the constant flood of new LLM application techniques can make any developer tired, certain patterns have proven consistently useful.
1. Decomposition
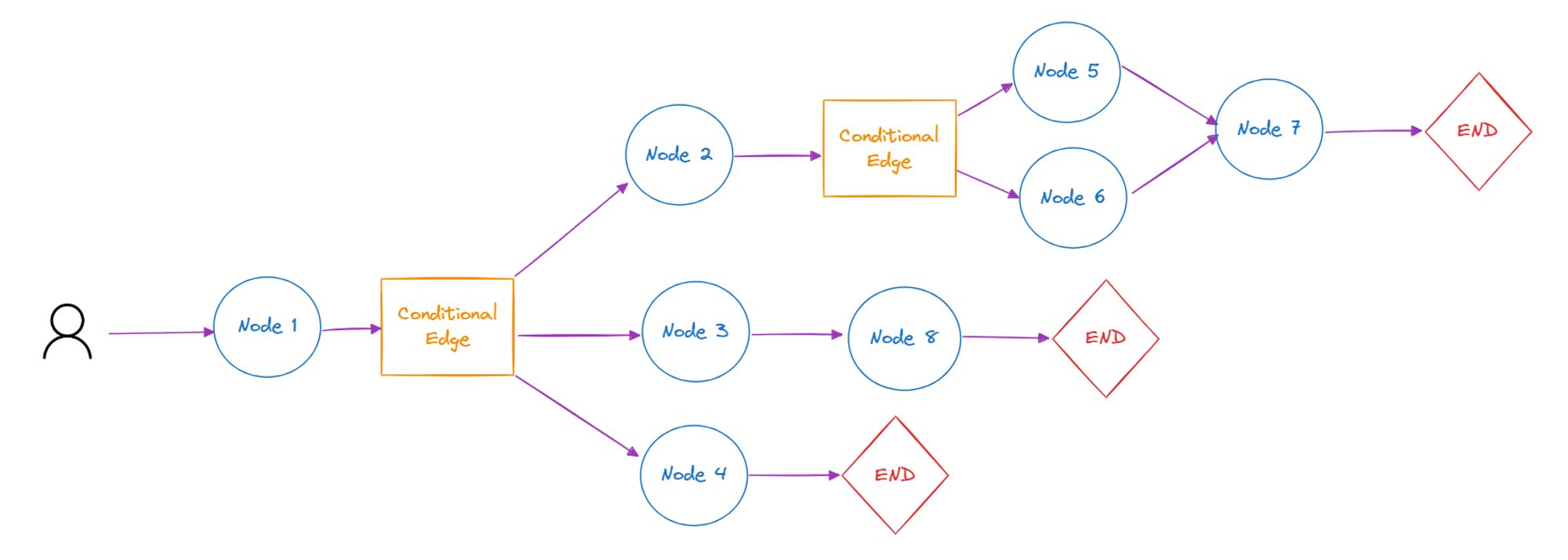
Big problems become less intimidating when broken into smaller chunks, and this is exactly the idea behind task decomposition. By dividing complex tasks into manageable subtasks, each part gets focused attention and just the right context, reducing risk for confusion and boosting performance. This approach also makes applications easier to debug and improve, since issues can be isolated to specific subtasks. For example, instead of creating multiple sets of instructions within the same prompt to handle different types of user input, the application can first determine the input type. Once identified, it can then use a prompt containing only the instructions relevant to that particular type.
2. Reasoning
Just like humans, LLMs often perform better when they first explore ideas, break things down, test concepts, and weigh possibilities before committing to an answer. Prompting the model to explain or justify its reasoning helps produce clearer, more accurate responses, particularly in contexts where logical reasoning and correct decision making is crucial.
3. Ensembling
The Ensembling Pattern, a staple strategy in the AI toolkit, continues to play a vital role with LLMs. By combining outputs from multiple models – or multiple runs of a single model – developers significantly improve reliability and accuracy. Commonly combined with reasoning for classification tasks, where ensembling allows LLM applications to explore diverse reasoning paths and see which option emerges as the most reliable or frequently selected, often enhancing classification accuracy and stability.
4. Iteration
Getting things right the first time isn't always easy, even for LLMs. The Iteration Pattern recognizes this, focusing on refining and improving initial outputs through multiple rounds of self-assessment and feedback. Each iteration can provide additional context, such as error messages or validation feedback generated by the LLM itself. This method works especially well for tasks like code generation, content creation, or detailed analyses, where initial outputs might require revisiting.
While the field of LLM-based applications moves quickly, these four patterns have withstood the test of time (and in the LLM world, this is measured in weeks 😛). Make sure to give these techniques a try if you haven't already. Of course, keep in mind there's often a trade-off between performance gains and the associated cost and run time – so choose carefully and implement only if needed!

Anton Wallgren
Tech lead
While crafting LLM applications, we've found out that a few patterns have proven consistently useful.
Let's work together
Ready to transform your data and AI capabilities? Get in touch with our team to explore how we can help.
Contact Us